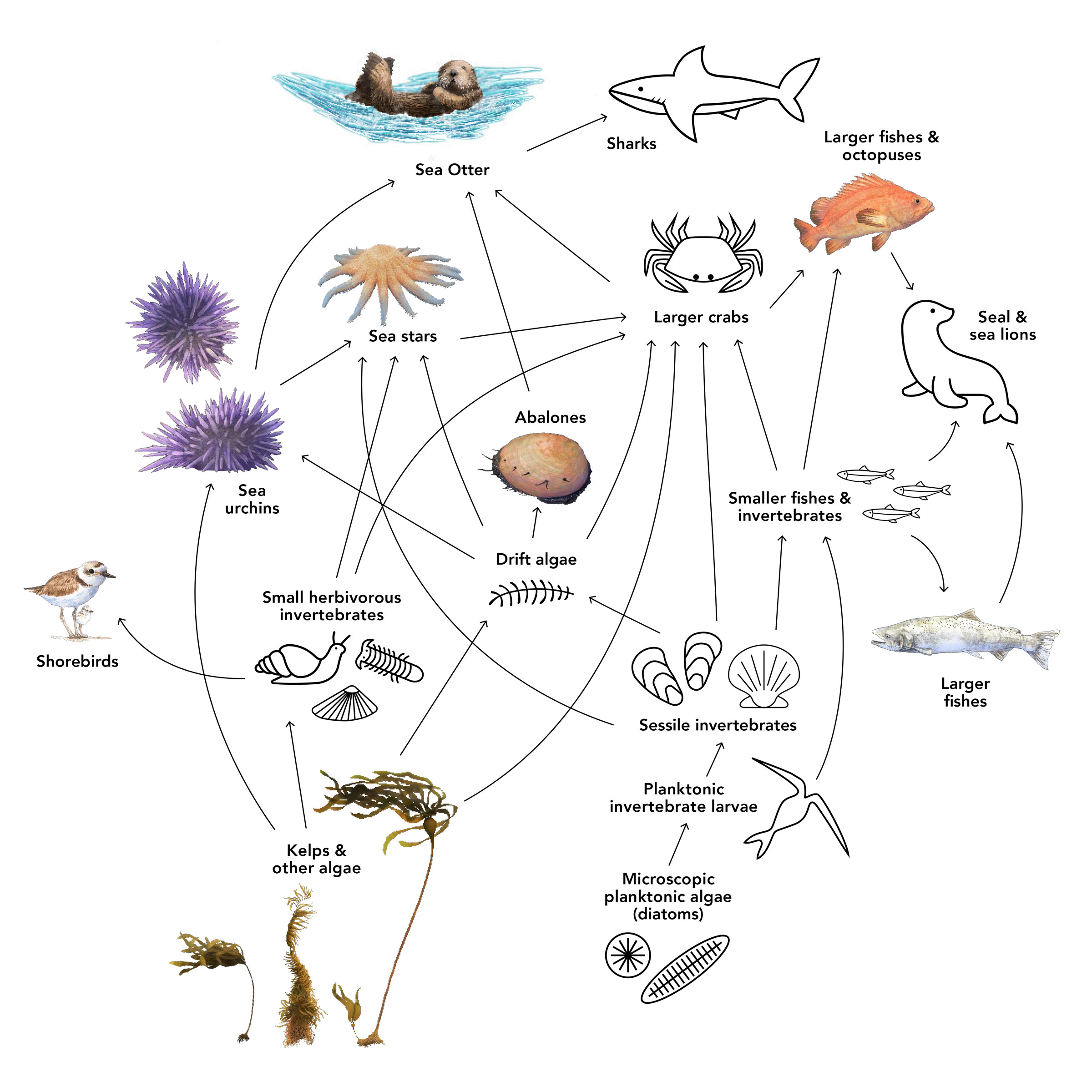
What Eats What
The bull kelp forest as a term signifies a web of interconnections between primary producers (seaweeds, kelps and single-celled microalgae) and a host of organisms both big and small that get eaten by other organisms. There are also the interactions between the foundational kelp and abiotic factors such as the ocean water itself (source of nutrients, more or less acidic, warmer or cooler), what the benthos or bottom is made of (rocky or sandy), the dynamics of wave action in a given cove or range of coastline, what humans have been doing along that coast, and complex interactions us humans can only guess at. A trophic cascade is when the effect of displacing one of the trophic (food) levels ripples throughout the ecosystem. Sea otter, sea urchin, and kelp form a classic trophic cascade.